The Evolution of AI in Healthcare
Key Milestones in AI Development
AI’s journey in healthcare began in the 1950s. Dartmouth College hosted the first AI conference in 1956, marking a starting point.
During the 1970s, the development of MYCIN, an AI program for diagnosing bacterial infections, showcased AI’s potential in healthcare.
Its success came from its ability to suggest treatment protocols based on symptom analysis, demonstrating early AI capabilities.
In 1997, IBM’s Deep Blue defeated chess champion Garry Kasparov, proving AI’s advanced problem-solving skills.
This milestone emphasized AI’s computational power, hinting at its potential for complex medical diagnoses.
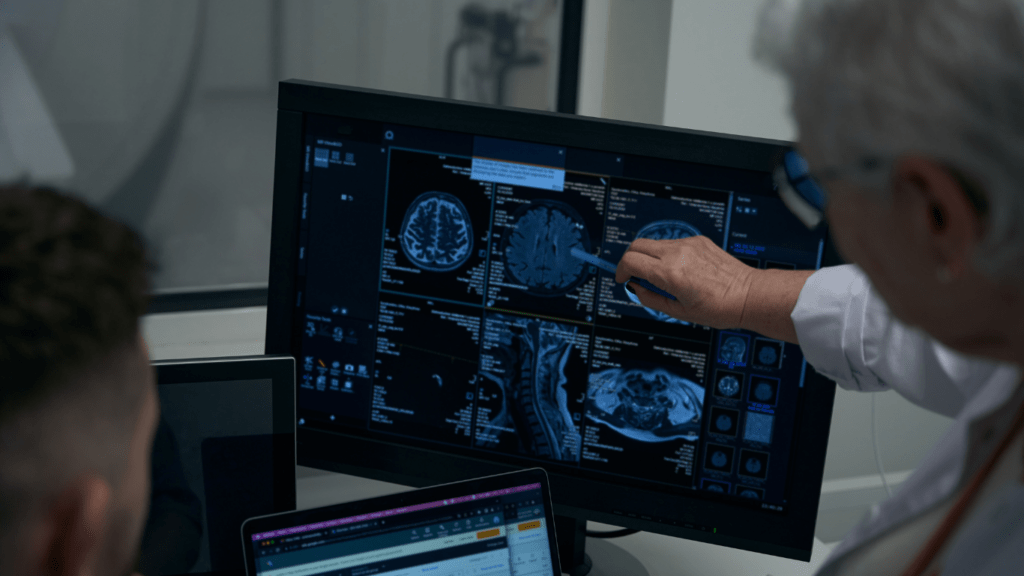
By the 2010s, deep learning advancements led to AI’s integration into image recognition tasks, aiding radiologists in interpreting medical images.
Impact on Early Diagnosis Techniques
AI significantly impacts early diagnosis techniques. Machine learning algorithms analyze patient data to identify patterns linked to diseases, often before visible symptoms appear.
For example, Google’s DeepMind Health utilizes AI to detect signs of eye diseases like diabetic retinopathy with high accuracy, revolutionizing early intervention strategies.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) further enhances diagnostic accuracy. It parses through electronic health records (EHRs), extracting critical information to aid in disease detection.
Companies like IBM Watson employ NLP to help oncologists diagnose and treat cancer by rapidly analyzing vast amounts of medical literature and patient data.
AI-powered wearable devices also contribute. They continuously monitor vital signs, alerting users and healthcare providers of potential health issues in real time.
Devices like Apple Watch and Fitbit use AI algorithms to detect anomalies in heart rhythms, allowing for timely medical intervention.
AI Advancements in Diagnostic Tools
1. Radiology and Imaging
AI is making significant strides in radiology and imaging. Machines with deep learning capabilities analyze radiographs, MRIs, and CT scans with high precision.
AI algorithms detect anomalies such as tumors, fractures, and infections faster than human radiologists in some cases.
For instance, in mammography, AI systems achieved sensitivity of around 94.5%, reducing false positives and false negatives substantially.
Automated image analysis frees up radiologists to focus on complex cases and improves workflow efficiency.
According to a study published in The Lancet Digital Health, AI solutions can help identify pneumonia in chest X-rays with an accuracy comparable to expert radiologists.
2. Genetic Testing and Personalized Medicine
AI’s role in genetic testing and personalized medicine is transformative. Machine learning models analyze genomic data to reveal mutations linked to specific diseases.
For instance, AI tools have identified genetic markers for conditions such as breast cancer and Alzheimer’s disease. Personalized treatment plans tailored to individual genetic profiles lead to better outcomes.
IBM Watson for Genomics is an example of AI leveraging genomic data to suggest targeted therapies for cancer patients.
By examining genetic variants, AI provides actionable insights, including:
- potential risks
- preventive measures
AI’s ability to analyze complex genetic datasets accelerates the path to personalized medicine, making treatments more effective and reducing adverse effects.
Treatment Personalization Through AI
1. Drug Development Innovations
AI is revolutionizing drug development by predicting potential drug candidates faster than traditional methods.
Machine learning models analyze vast datasets, identifying patterns and relationships that might take years for researchers to discern.
For instance, DeepMind’s AlphaFold has accurately predicted protein structures, expediting the development of novel drugs.
Additionally, AI algorithms simulate how different compounds interact with biological targets, streamlining the preclinical phase.
These advancements reduce the time and cost associated with bringing new drugs to market, making personalized treatments more accessible.
2. Surgical Robotics and Assistance
AI-enhanced surgical robots are elevating the precision and efficiency of surgical procedures.
These robots, equipped with advanced imaging and machine learning capabilities, assist surgeons in performing complex operations with pinpoint accuracy.
For example, the da Vinci Surgical System allows for minimally invasive procedures, reducing recovery times and minimizing risks.
AI algorithms provide real-time data analysis during surgery such as:
- offering insights
- alerts to enhance decision-making
As AI continues to evolve, it’s expected to further refine surgical techniques, improving patient outcomes and paving the way for more personalized surgical care.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
Data Privacy and Security
AI’s integration in healthcare raises significant concerns about data privacy and security. Patient data is highly sensitive, encompassing personal information, medical histories, and genetic data.
Ensuring data protection is crucial to maintaining patient trust and complying with regulations like HIPAA in the US and GDPR in Europe.
Healthcare providers and AI developers need robust encryption and anonymization protocols when handling patient data.
Moreover, any data breaches can lead to severe consequences, including financial penalties and loss of patient trust.
Bias and Reliability in AI Systems
Bias and reliability in AI systems pose critical challenges in healthcare. AI models, trained on existing medical data, can inadvertently learn and propagate biases present in that data.
For instance, if training datasets lack diversity, AI might underperform in diagnosing diseases across different demographic groups.
This can compromise the reliability of AI applications in clinical settings. Continuous monitoring and updating of AI models are necessary to mitigate bias and enhance reliability.
Efforts to include diverse datasets and implement fairness algorithms are essential to ensure equitable and accurate healthcare solutions.

